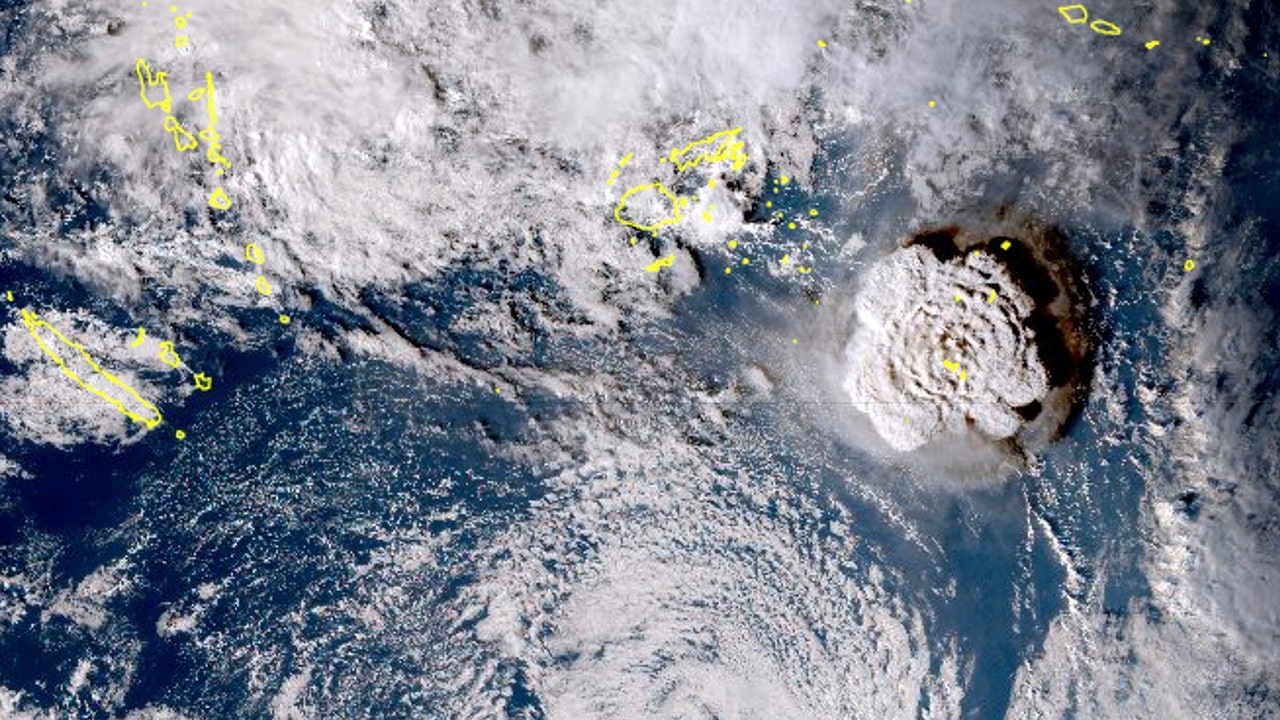
Tonga undersea volcano eruption disrupted satellite signals halfway around the world, researchers say
Fox News
The submarine eruption of Tonga's Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano last year reportedly disrupted satellite signals halfway around the world, according to scientists.
An equatorial plasma bubble, or EPB, can delay radio waves as well as degrade the performance of GPS. Disruptions to the ionization of the ionosphere, where molecules and atoms are ionized by solar radiation, and subsequent creation of a density gradient of electrons can cause the formation of the EPB. Julia Musto is a reporter for Fox News and Fox Business Digital.
Japan's Nagoya University noted in a news release that the area of the ionosphere with the highest concentration of ionized particles is called the F-region, which is located 150 to 800 kilometers above the surface of the Earth. The region plays a crucial role in long-distance radio communication.













