The Svedberg show Premium
The Hindu
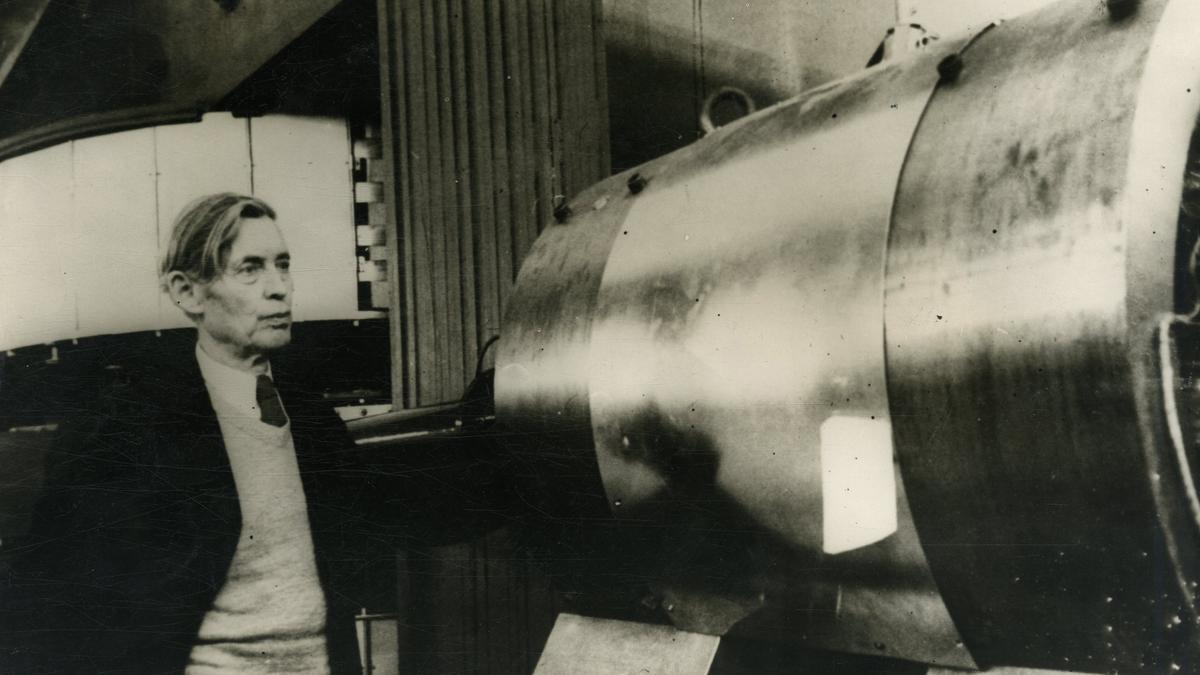
Theodor Svedberg, more commonly referred to as just The Svedberg, is a Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1926 winner “for his work on disperse systems.” He applied for one of his early patents on June 1, 1909, and spent a lifetime working with colloids, in addition to inventing the ultracentrifuge. A.S.Ganesh tells you more about The Svedberg…
Born on August 30, 1884 at Flerang in the parish of Valbo near Gavle, Sweden, Theodor (The) Svedberg was the only child of Elias Svedberg and Augusta Alstermark. The fact that his father was a works manager at different ironworks in Sweden and Norway meant that the family lived at a number of places in Scandinavia during his childhood. His father made it a point to take him out for excursions often, allowing him to develop a love for nature and a keen interest in botany.
Svedberg attended the Koping School, the Orebro High School and Gothenburg Modern School and had the privilege of being taught by some prominent teachers. These teachers were also understanding, allowing Svedberg to study on his own. This gained him access to laboratories after ordinary classes and Svedberg spent time in the afternoons at the physical and chemical labs of the school.
Stoked by the advent of new discoveries and inventions in both physics and chemistry, Svedberg went about building stuff on his own. He created a Marconi-transmitter and a Tesla-transformer this way and even arranged public demonstrations that included wireless telegraphy between two blocks of his school.
Even though he had a passionate interest in botany, he decided to study chemistry following his hands-on efforts in his school laboratories. This experience also put him in good stead when he went on to experiment with colloids later on.
After matriculating from school, Svedberg began a lifelong association with Uppsala University in January 1904. It was here that he received his Bachelor of Arts degree in 1905, his Master’s degree in 1907 and Doctor of Philosophy in 1908.
While still studying, Svedberg accepted a post as assistant in the Chemical Institute at Uppsala. This means that Svedberg’s scientific career set off in 1905, while he was still in his early 20s. By 1907, he was given the added responsibility of serving as lecturer in chemistry in the university. It wasn’t long before a special appointment as lecturer and demonstrator of physical chemistry came through in 1909. In 1912, he was elected Professor of Physical Chemistry, Uppsala University – a position he held onto until 1949, when he was made emeritus.
It was in 1949 that Svedberg took on the role of director of the Gustaf Werner Institute for Nuclear Chemistry at the University. He remained at this post until 1967 and the institute was renamed The Svedberg Laboratory in 1986, about 15 years after his death in 1971. The facility was permanently shut down in 2016, following a decision a year earlier to implement decommissioning.

Reflect is a thematic art quilt exhibition in Chennai by The Square Inch and the Quilt India Foundation, featuring 58 juried quilts that explore reflection through fabric. Held at Sri Sankara Hall, Alwarpet, from January 23 to 26, the show highlights contemporary quilt art, including Double Wedding Ring and Rolling Waves quilts displayed in India for the first time.












