How simulation using AR, VR can facilitate learning Premium
The Hindu
Simulations in education, from earth-sun-moon system to antimicrobial resistance, enhance learning through interactive virtual experiences.
Simulations in education are teaching strategies that mimic real-life scenarios of events or processes. They aid in a clear understanding of concepts and have been an integral part of science classrooms for decades. The earth-sun-moon system is a classic example that can be simulated using a role-play method, where students assume the roles of the earth, the sun and the moon to learn concepts like earth’s rotation, phases of the moon, eclipses, and so on.
How does one learn abstract concepts such as evolution, cell structure, or chemical reactions in a classroom? Online simulations to the rescue!
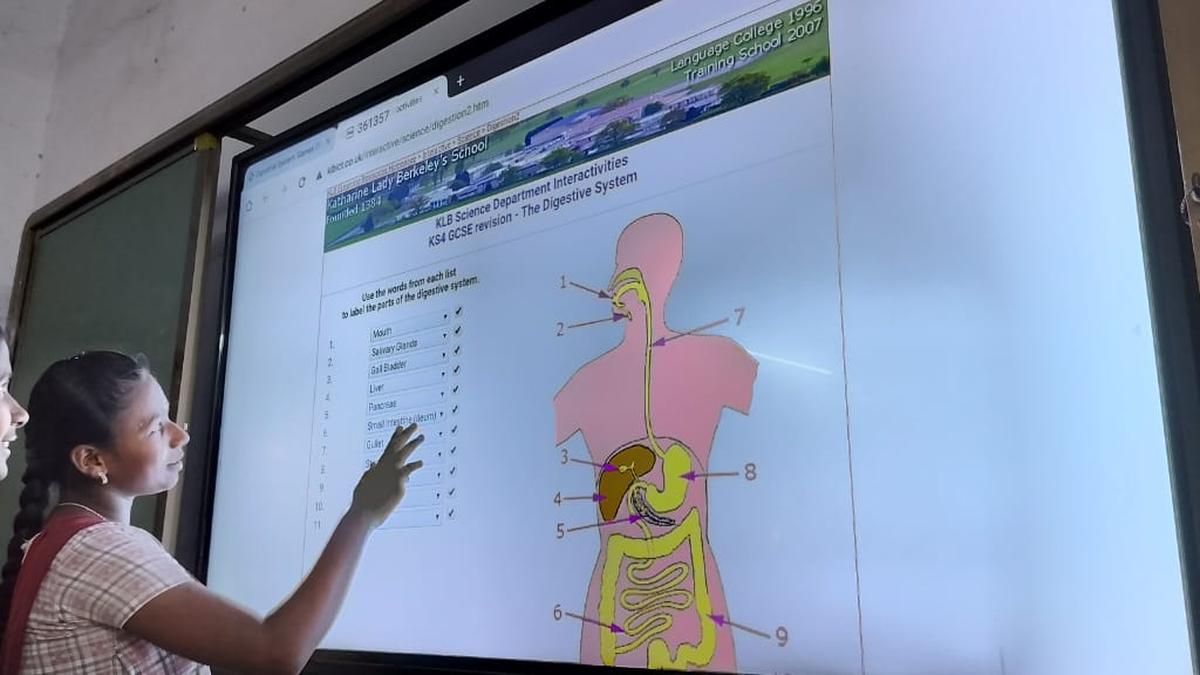
Simulations provide opportunities for students to observe, evaluate, and explore. Thanks to technological advancements, online tools such as agent-based models (ABM), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR)-based simulations have made it possible to simulate processes and concepts ranging from microbiology to astronomy in the sciences. Most online simulations are based on the inquiry-based 5E-instructional model- engage, explore, explain, elaborate, evaluate.
Agent-based models simulate the actions of ‘agents,’ which are the components of a simulation. Agents could be molecules, cells, or animals in a system. For example, suppose a teacher wants to teach the spread of a virus within a population. In that case, an ABM such as NetLogo* provides a digital space where the students can set up a model to change the number of viral particles, population density, or chances of recovery of infected persons and observe how the infection is transmitted over a given period.
Such models engage students in collecting data, analysing graphs and understanding how individual actions lead to outcomes at the system level. Teaching topics in physics such as electricity or optics can also be simplified due to simulations such as PhET. ABMs give a real-life experience to students, where they can manipulate variables to gain an interactive learning experience.
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that blends digital information with a learner’s real-world experience. For example, astronomy teachers could use mobile applications that simply require a mobile phone to be held against the sky. The application shows all the information about celestial objects in the direction to which the in-app camera is pointed. AR is also widely used to teach chemistry, anatomy, or concepts where real-life resources are unavailable or could pose a hazard to students. Most AR-based tools require minimal resources, such as a mobile, laptop or a tablet and internet connection.
Virtual reality or VR creates an entirely virtual representation of an environment. While it provides a fully immersive and highly engaging learning experience, it requires sophisticated VR laboratories equipped with VR headsets.













