Stanford study finds largest recorded Alberta earthquake likely caused by oilsands wastewater
Global News
The largest recorded earthquake in Alberta's history was not a natural event, but most likely caused by disposal of oilsands wastewater, new research has concluded.
The largest recorded earthquake in Alberta’s history was not a natural event, but most likely caused by disposal of oilsands wastewater, new research has concluded.
“This event was caused by wastewater disposal,” said Ryan Schultz, a Canadian seismologist who helped conduct the research while at Stanford University in California.
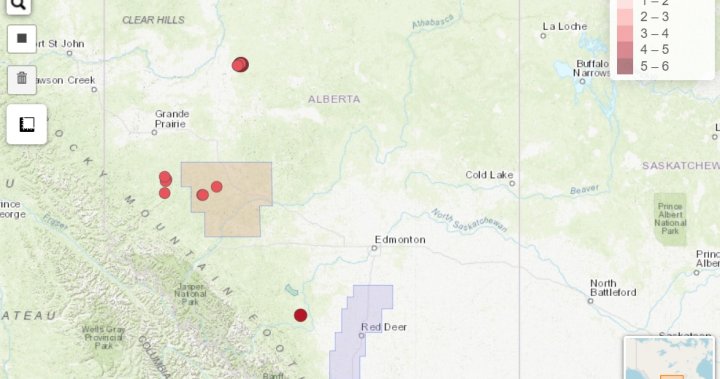
In November, parts of Alberta near the northwestern town of Peace River were rocked by a series of quakes culminating in one that reached a 5.6 magnitude.
Residents reported being knocked to their knees. The earth was pushed upward by more than three centimetres — enough to register on satellites.
Oilpatch techniques, such as deep disposal wells that inject wastewater kilometres underground, can induce earthquakes. One such well located near the earthquake site, used to dispose of water used in oilsands operations, has injected more thanone millioncubic metres of wastewater down about two kilometres.
After the record-breaking quake occurred, the Alberta Geological Survey, a branch of the province’s energy regulator, attributed it to natural causes. The centre of the quake, then estimated to be six kilometres underground, was thought too deep and too far away from oilpatch activity in time and space to have been generated by industry.
Not so, said Schultz.
A closer and more thorough look at the data brought the centre of the quake up to about four kilometres beneath the surface. That figure is now reflected in the regulator’s catalogue of Alberta quakes.

Annette Dionne, the last of the famous ‘Dionne Quintuplets’ died in a suburb of Montreal on Wednesday, at the age of 91. Dionne’s death was first reported by the New York Times. A family spokesperson, told the publication she died due to complications related to Alzheimer’s disease. The Dionne Quints Home Museum in North Bay,...












