Heart repair without surgery: The TEER procedure
The Hindu
Heart repair without surgery: The TEER procedure
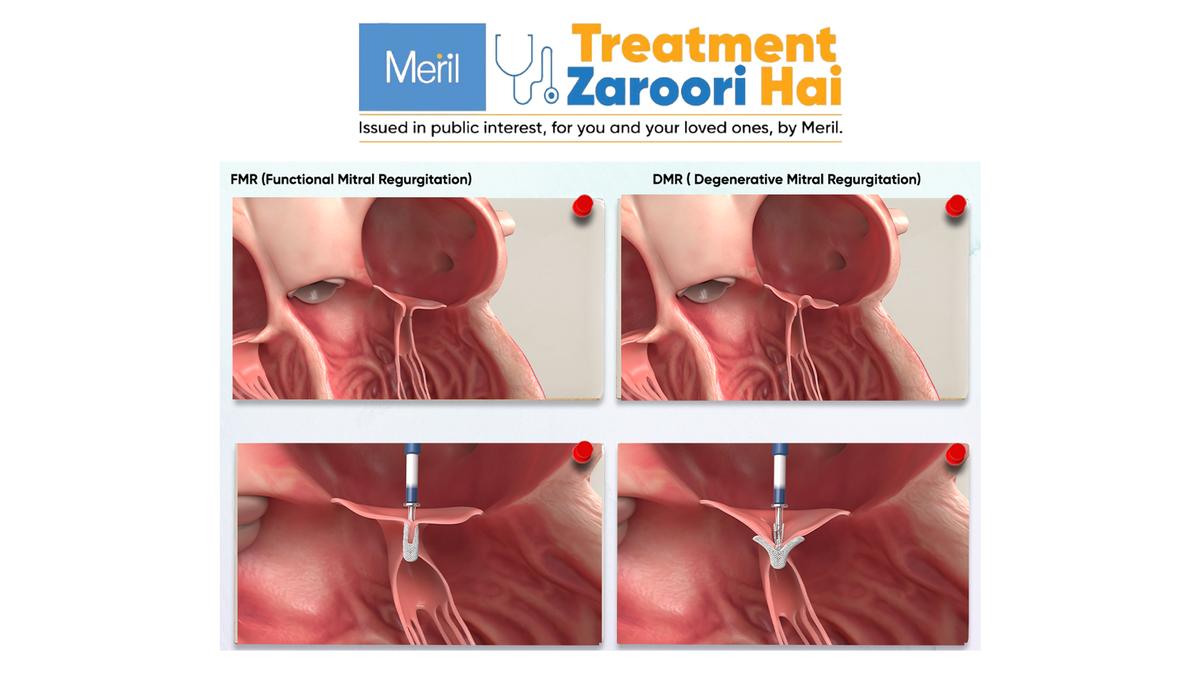
Mitral Valve Leakage, also known as mitral regurgitation, is a symptomatic, cardiovascular condition wherein the mitral valve does not close tightly. This causes blood to flow backwards into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts and onwards in towards the lungs causing severe blood pressure and symptoms. This is a serious heart condition usually observed in patients who have experienced heart attacks and have a dilated heart but can also occur in patients who are elderly and have diseased mitral valve which do not close properly. Reportedly more than 70% of the population on conventional medical treatment may die in case they are not offered treatments such as valve replacement, mitral annular surgery or TEER procedure.
The Mitral Valve is a unidirectional valve located between the left atrium and the left ventricle, and it facilitates the flow of purified / oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the body. In a healthy heart, the mitral valve opens and closes tightly with each heartbeat preventing the blood flowing in reverse direction towards the lungs. When the mitral valve does not close tightly, the blood flows back into the left atrium, and the heart compensates for the blood leakage by pumping harder, masking the issue in the early years. As the severity of blood leakage increases with years within a few years it leads to compromised heart conditions which is irreversible and eventually fatal.
The common observed causes for Mitral Valve Leakage are Degenerative Mitral Valve disease caused due to progressing age, atrial fibrillation, Rheumatic fever from untreated gum or throat infection, Heart attacks that cause damage to valve structures, Infective endocarditis, also known as Valve infection, and Congenital valve defects that arise due to birth defects.
The early symptoms of the disease are usually observed at the age of 60 years and above.
Mitral Valve defect can be diagnosed early through:
Early detection of the disease allows surgeons to manage the symptoms with medication and to avoid heart failure or atrial fibrillation.
For managing mild symptoms, surgeons usually prescribe medicines such as Diuretics to reduce fluid build-up, and Beta-Blockers and ACE inhibitors to improve heart function. Other newer medications include ARNI, SGLT-2 inhibitors which also improve heart function. In some patients where the pumping capacity of the heart is sufficient (>30%) the surgery may be considered. In majority of these patient the pumping capacity is severely compromised (













